See also the -T option. Use ' make ' to configure for your OS and compile the source code. If the total aggregate bandwidth is more than what an individual stream gets, something is wrong. If non-zero, a report is made every interval seconds of the bandwidth since the last report. Open JPerf by clicking on jperf. This doesn't qualify as a proper answer but have you tried ensuring that the iperf version on the Solaris end matches the one you are running on Windows. Iperf works by writing an array of len bytes a number of times.
| Uploader: | Voodoogis |
| Date Added: | 6 February 2010 |
| File Size: | 7.96 Mb |
| Operating Systems: | Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X |
| Downloads: | 33042 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
In that case, datagrams sent before the server started show up as losses in the first periodic report 61 datagrams on arno below. The default size of bytes works for ethernet.
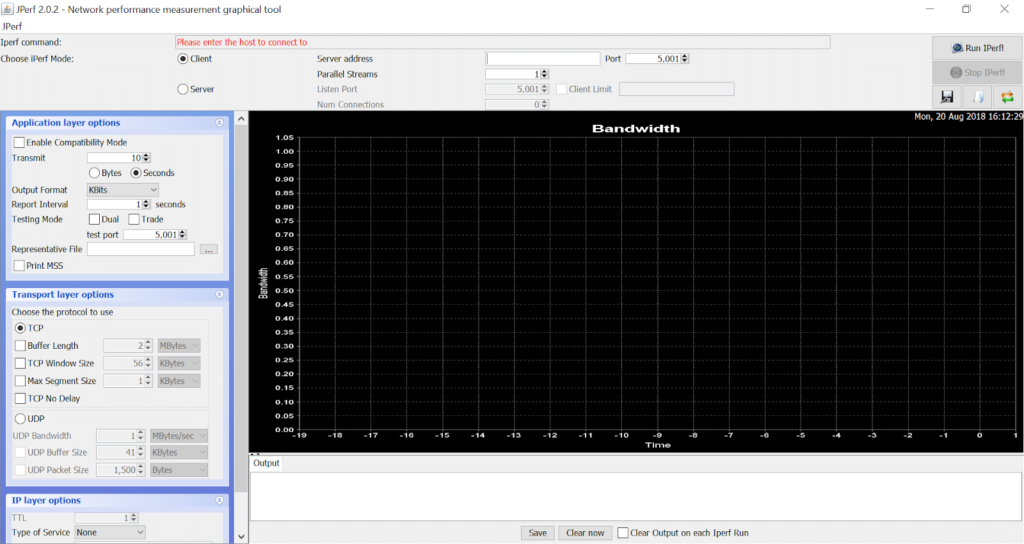
How to Use JPerf | NetBeez
This doesn't qualify as a proper answer but have you tried ensuring that the iperf version on the Solaris end matches the one you are running on Windows. The server port for the server to listen on and the client to connect to. The problem lies that the old client will always report say "42" and the new client will always report say "95". You might try the iperf-users mailing list archives, or even posting your question there.
Note for UDP, this is the datagram size and needs to be lowered when using IPv6 addressing to or less to avoid fragmentation. The best answers are voted up and rise to the top. A quick analysis of the window size through the exchange shows the old iperf moving back and forth but mostly at 32k while the new iperf mostly keeps at 64k.
Run Iperf in tradeoff testing mode.
The client's and server's clocks do not need to be synchronized; any difference is subtracted out in the jitter calculation. This is essentially the number of router hops to go through, and is also used for scoping.
There could be some other code difference between 1. Redirect the output to a file.
Iperf version 1.7.0
You can do this by running it on Linux or any other operating system as a server or a client. Start multiple clients or servers as explained above, sending data to the same multicast server. And then accept the answer once the minimum time requirement elapses. From my testing launching iperf old with window size "x" and iperf new with window size "x" instead of producing the same or very close results produce totally different results. Jitter is the smoothed mean of differences between consecutive transit times.
By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Cookie PolicyPrivacy Policyand our Terms of Service. In more detail, here are the files that need to be copied from the unzipped iPerf 2.
Prints 'pthreads' if compiled with POSIX threads, 'win32 threads' if compiled with Microsoft Win32 threads, or 'single threaded' if compiled without threads. This is done following the client connection termination, therefore running the tests alternating.
This is only useful on multihomed hosts, which have multiple network interfaces.
For UDP it is just the buffer which datagrams are received in, and so limits the largest receivable datagram size. This is a very artificial stream, similar to voice communication but not much else.
Home Questions Tags Users Unanswered.
networking - Different versions of iperf for windows give totally different results - Server Fault
See also the -l and -n options. The server computes the relative transit time as server's receive time - client's send time. You may specify the value in hex with a '0x' prefix, in octal with a '0' prefix, or in decimal.
Open JPerf by clicking on jperf. Here is how the jperf The type-of-service for outgoing packets. These may be as low as 64 KB, or as high as several MB.

I don't know if either of them are accurate. This widows have a UDP client -u sending to the multicast address So K instead of bytes.

Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий